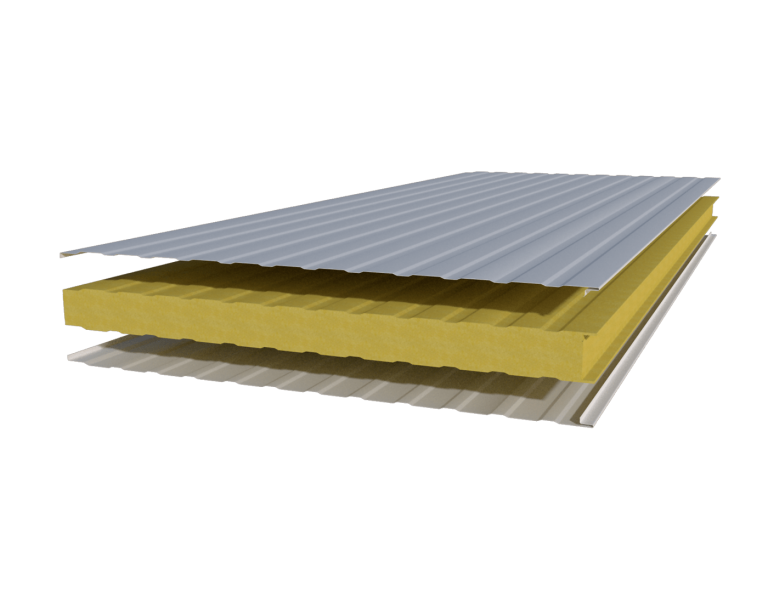
In the last few decades, sandwich panels have proved to be a revolutionary solution in the construction industry. Nowadays, sandwich panel has become the most commonly used building material for industrial, commercial, sports, agricultural, and public buildings. It is also used to build partition walls, ceilings, and other partitions in various types of buildings.
There are 8 reasons to choose sandwich panels
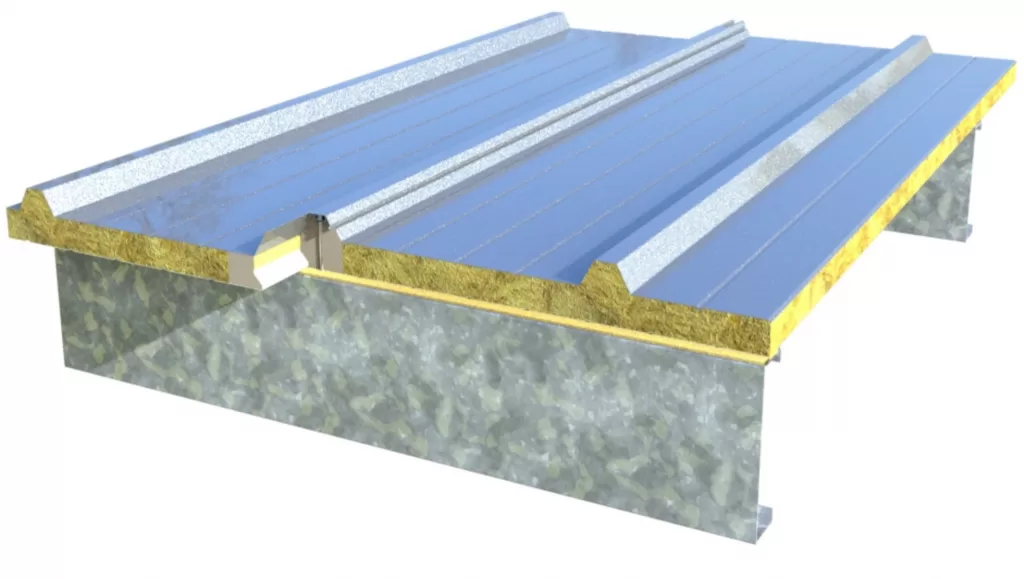
1. Excellent Insulation: Sandwich panels consist of two outer layers (skins) and a core material in between. The core material is typically an insulating material such as expanded polystyrene (EPS), polyurethane (PU), or mineral wool. This design provides excellent thermal insulation properties, making sandwich panels ideal for applications where temperature control is important, such as in building construction or refrigeration.
2. Lightweight: Sandwich panels are lightweight compared to other construction materials, such as concrete or solid steel. This characteristic makes them easier to handle, transport, and install, reducing construction time and costs. Additionally, the lightweight nature of sandwich panels can lead to overall weight savings in structures, which can be advantageous in applications such as transportation vehicles or aerospace.
3. Strength and rigidity: Despite their lightweight nature, sandwich panels offer high strength and rigidity. The combination of the outer skins and the core material creates a structure that can withstand significant loads and stresses. This makes sandwich panels suitable for applications that require structural integrity, such as building facades, partition walls, or industrial enclosures.
4. Versatile Application: Sandwich panels are available in various sizes, shapes, and thicknesses, offering versatility in design and application. They can be customized to meet specific requirements, allowing for flexibility in architectural and industrial projects. The panels can also be easily cut, shaped, and assembled, making them adaptable to different construction needs. Sandwich panels are available in wall and roof versions, which are typical for the following types of structures:
- Warehouses and logistic hubs
- Cold stores
- Production facilities
- Sport facilities
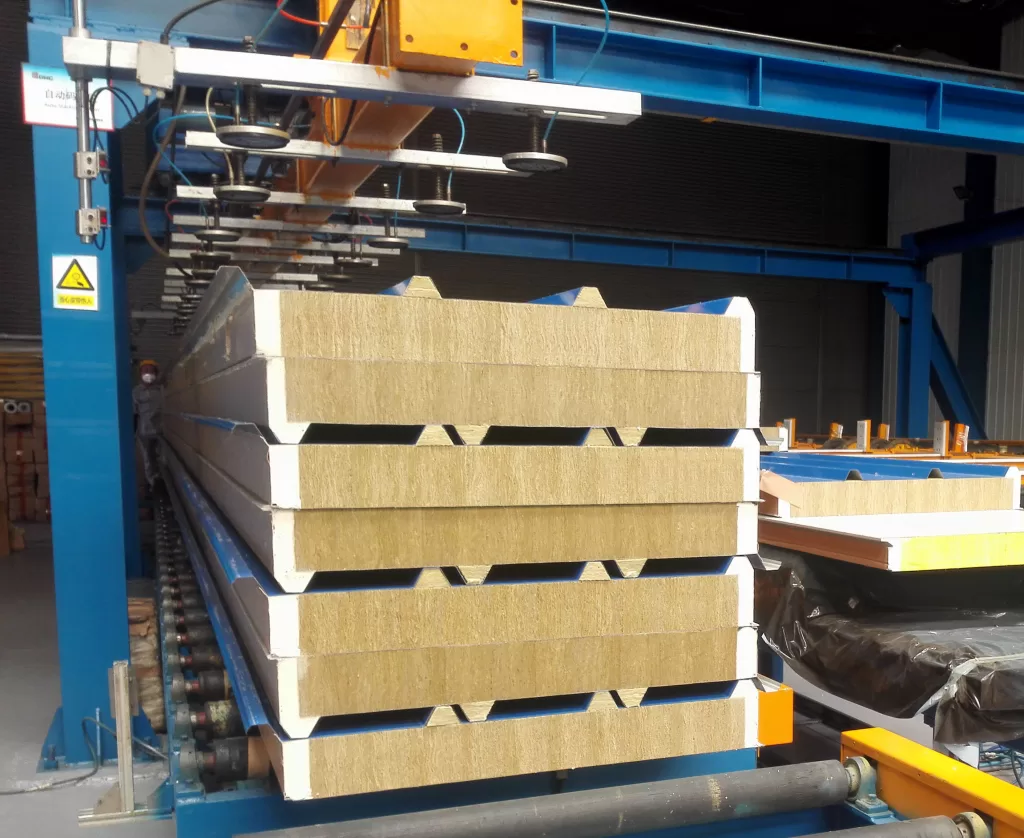

5. Energy efficiency: Due to their excellent thermal insulation properties, sandwich panels contribute to energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer between the interior and exterior environments. This can lead to lower heating and cooling costs in buildings, making them more environmentally friendly and cost-effective in the long run.
6. Acoustic insulation: Sandwich panels with appropriate core materials can provide effective acoustic insulation. They can minimize the transmission of sound waves, reducing noise pollution and improving acoustic comfort in buildings or other applications where noise control is essential, such as recording studios, theaters, or industrial facilities.
7. Fire resistance: Depending on the core material used, sandwich panels can offer good fire resistance properties. Some core materials are inherently fire-resistant, while others can be treated with fire-retardant additives to enhance their fire performance. This makes sandwich panels a viable choice in applications where fire safety is a concern, such as commercial buildings, warehouses, or data centers.
8. Diverse Materials: Sandwich panels come in various basic variants, each utilizing a specific panel core material to meet specific needs. The most common core materials used in sandwich panels are polyurethane (PU), mineral wool, and expanded polystyrene (EPS). Yes, you are correct. Sandwich panels come in various basic variants, each utilizing a specific panel core material to meet specific needs. The most common core materials used in sandwich panels are polyurethane (PU), mineral wool, and expanded polystyrene (EPS). Here’s a brief overview of these core materials.
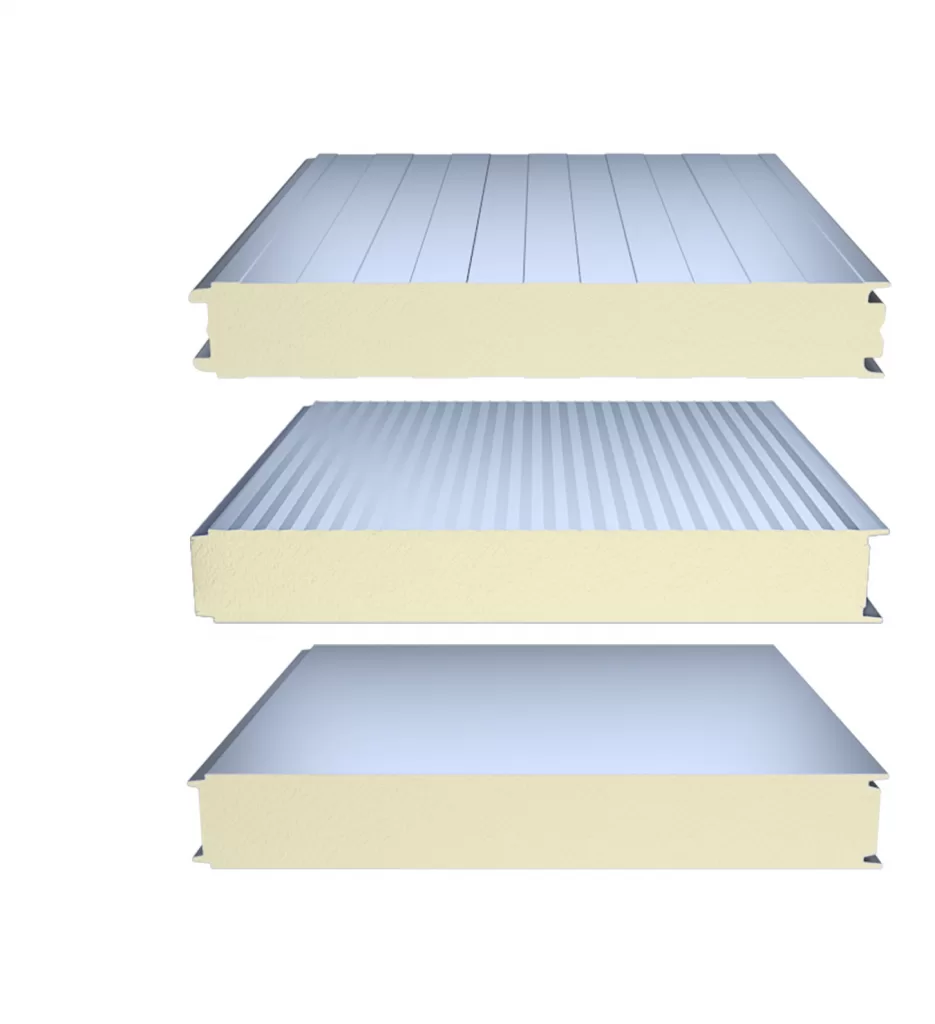
Polyurethane (PU) Core:
- Thermal insulation
- Structural strength
- Energy efficiency
Mineral Wool Core:
- Fire resistance
- Acoustic insulation
- Thermal insulation
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Core:
- Cost-effective insulation
- Light-weight construction
- Moisture resistance