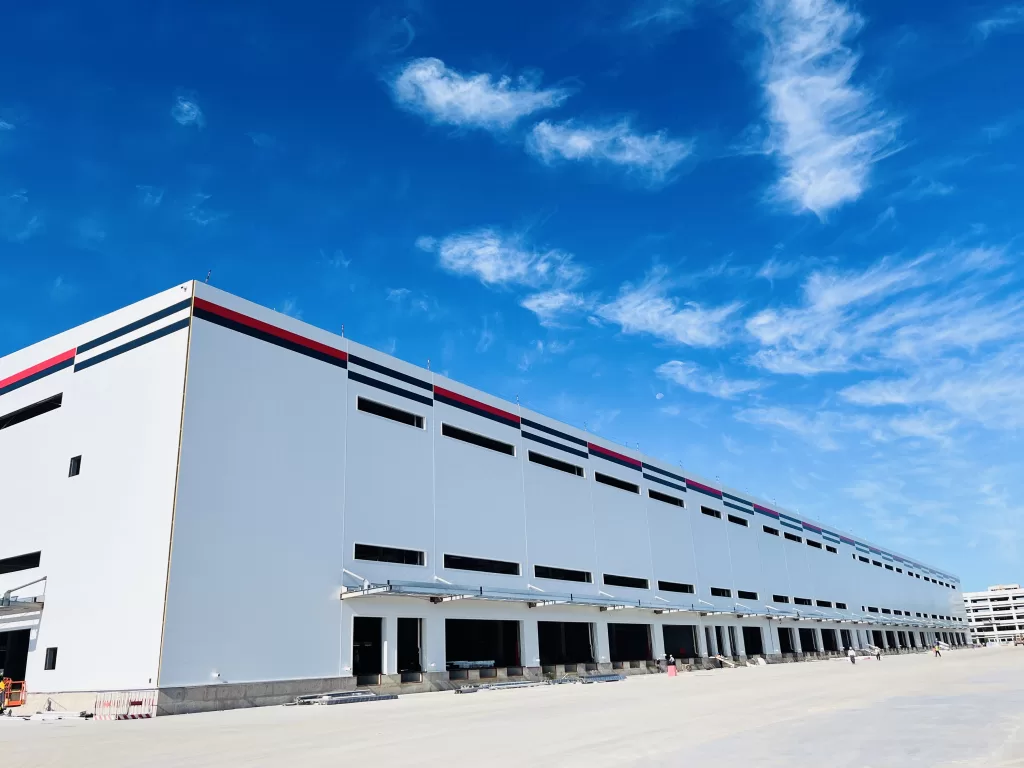
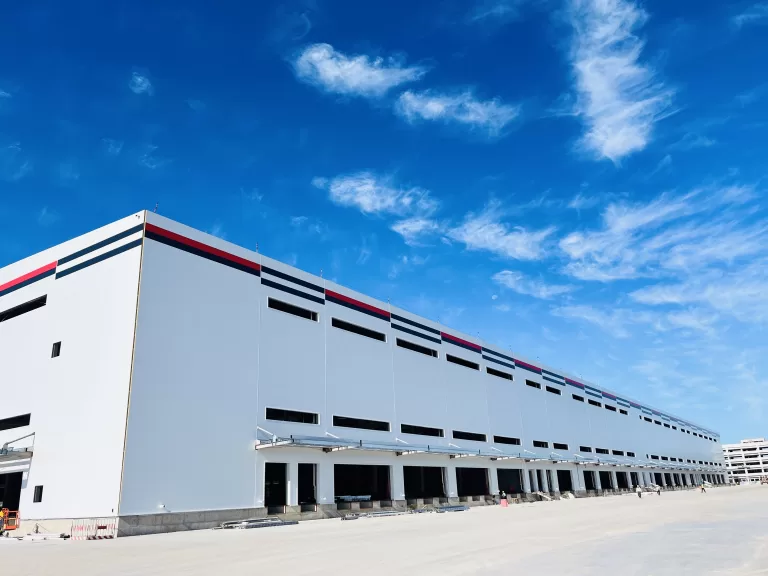
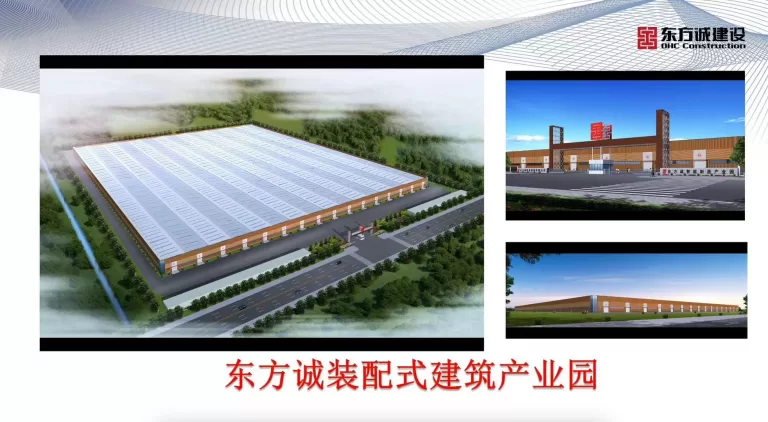
Sandwich panels are a fascinating innovation in construction and manufacturing. Consisting of a lightweight core material sandwiched between two layers of a more rigid material, these panels offer exceptional strength and insulation properties. The fabrication process typically involves several key steps:
- Material Selection: Choosing the appropriate core material (e.g., foam, honeycomb, or mineral wool) and facing materials (e.g., aluminum, steel, or fiberglass) is crucial for achieving the desired performance characteristics.
- Preparation: The facing materials are prepared by cutting them to size and possibly shaping them to fit the desired dimensions and contours of the panel.
- Assembly: The core material is sandwiched between the facing materials using specialized adhesives or bonding techniques. This step requires precision to ensure proper alignment and bonding of the layers.
- Pressing or Bonding: The assembled sandwich panel is typically subjected to heat and pressure in a press or bonding machine. This process ensures a strong bond between the layers and helps to consolidate the panel structure.
- Finishing: Once the bonding process is complete, the sandwich panel may undergo additional finishing processes such as trimming, sanding, or painting to achieve the desired appearance and surface quality.
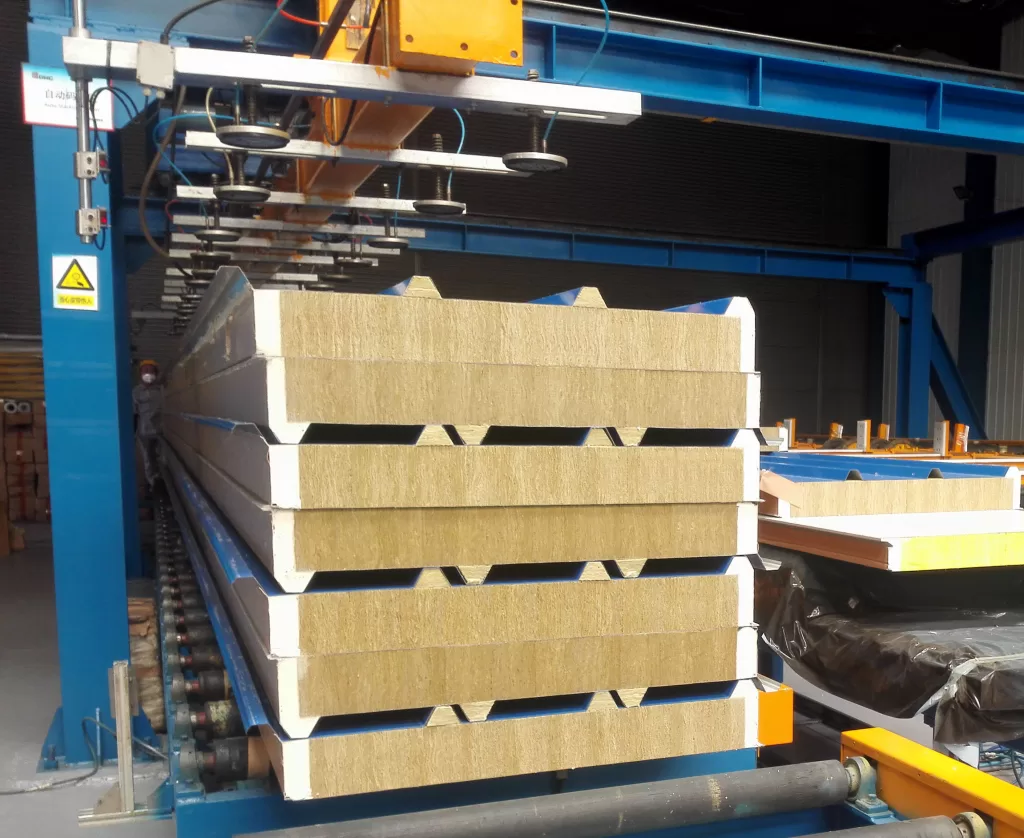

The fabrication of sandwich panels requires expertise in materials science, manufacturing processes, and engineering principles. However, the resulting panels offer numerous benefits, including lightweight construction, excellent thermal and acoustic insulation, and structural integrity. From building facades to refrigerated transport vehicles, sandwich panels are used in a wide range of applications, making them a versatile and valuable solution in modern manufacturing and construction.